Joins use more shuffles than any other process in Spark. It always leads to bad performance
Broadcast Hash Join (Map Side Join/ Replicated Join)
- Used when we want to compare a small and large table
- The entire small table is copied into each partition location of the large table
- The table joining happens in the mapper stage itself
- Default: 10 Mb (Max size of small table)
# Force broadcast an table
empDF.join(broadcast(deptDF), empDF.emp_dept_id == deptDF.dept_id, "inner").show()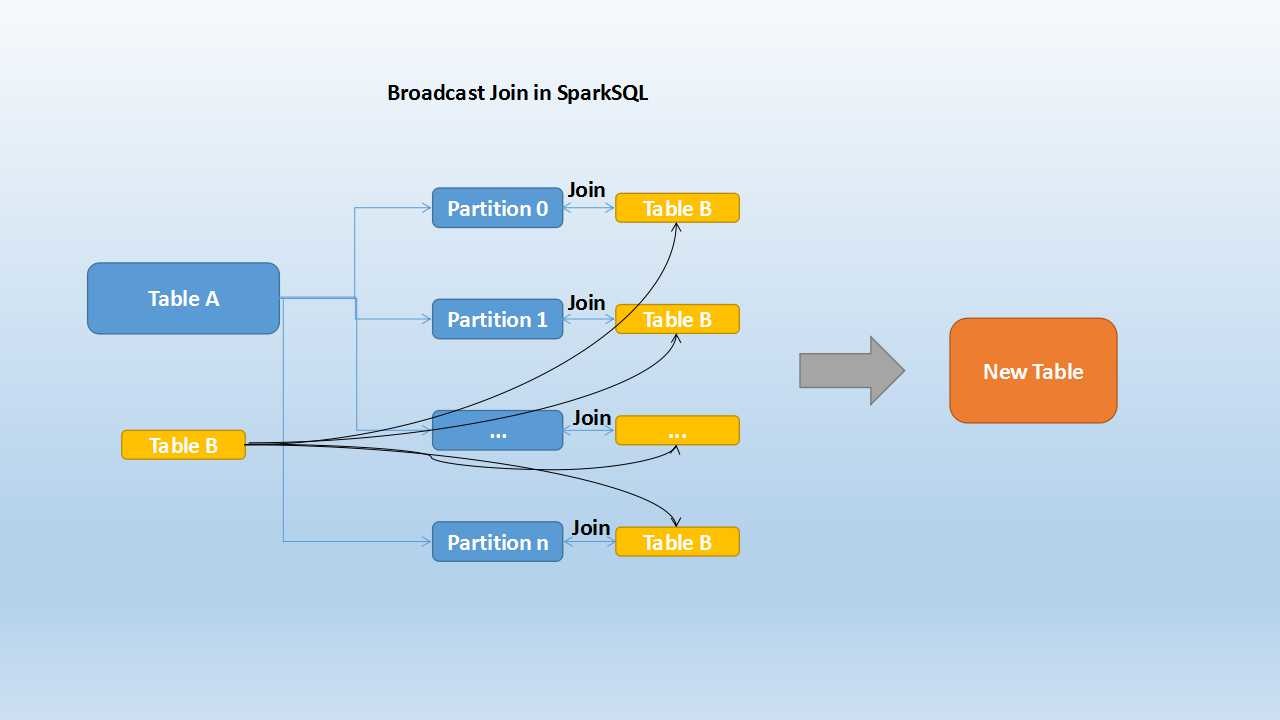
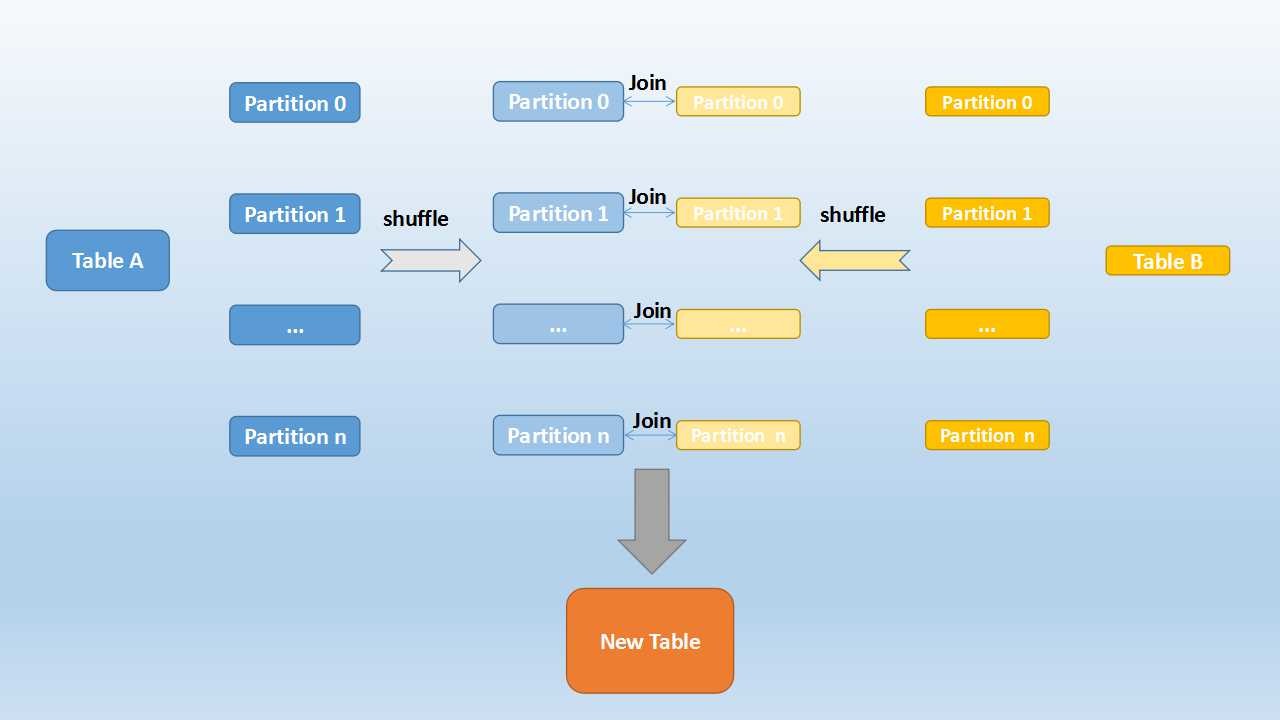
Shuffle Hash Join
- Used when we join 2 large tables
- The partitions are shuffled to get similar data together (Done for both table)
- And then this shuffled partitions are joined together
- The values that going to be in a partition after shuffle is decided by hash function
- Used for non-indexed data
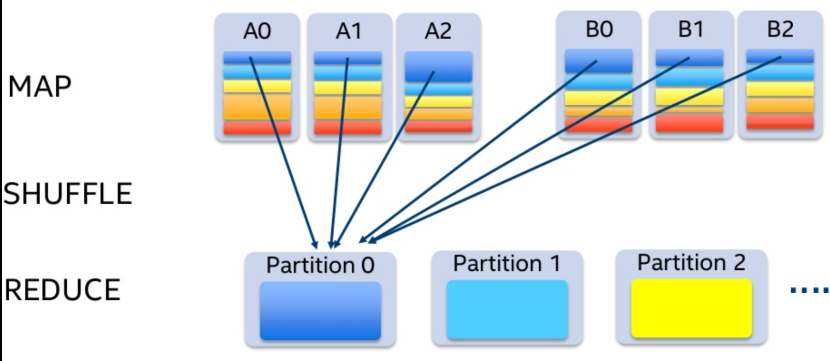
If we try to join normally for similar data we need to access all the partitions and then are join and reduced into a new partition
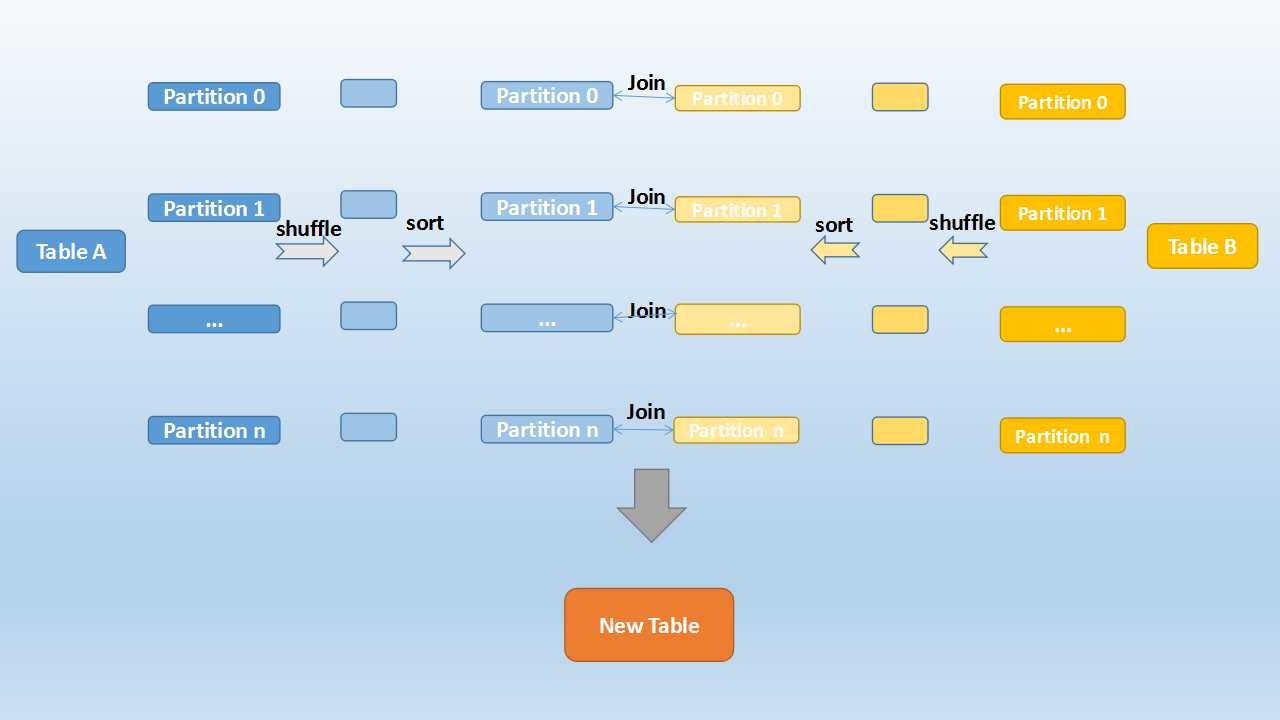
Sort Merge Join
- Used to join very large tables
- Groups the same keys to the same partition
- It is the default sort strategy in Spark since v2.3
- The join key needs to be orderable (sortable) for this algorithm to work
Joins in Spark SQL- Shuffle Hash, Sort Merge, BroadCast -24 Tutorials