It is a network protocol that controls how data is transmitted over LAN (IEEE 802.3)
Ethernet uses a contention-based approach to determine which device will use the network
While contention-based networks can lead to collisions, they have lower overhead compared to deterministic networks where an electronic token would need to be passed around for devices to use the network
It uses CSMA-CD to detect if the medium is empty
Ethernet Header
Contains Source MAC Address, Destination MAC Address, EtherType and Optional VLAN Tag
EtherType fields are used to denote if the payload is using IPv4 or IPv6
Payload is the encapsulated data that is received from the Network Layer
The payload has a minimum size of 42 bytes if VLAN and 46 bytes if VLAN is not used
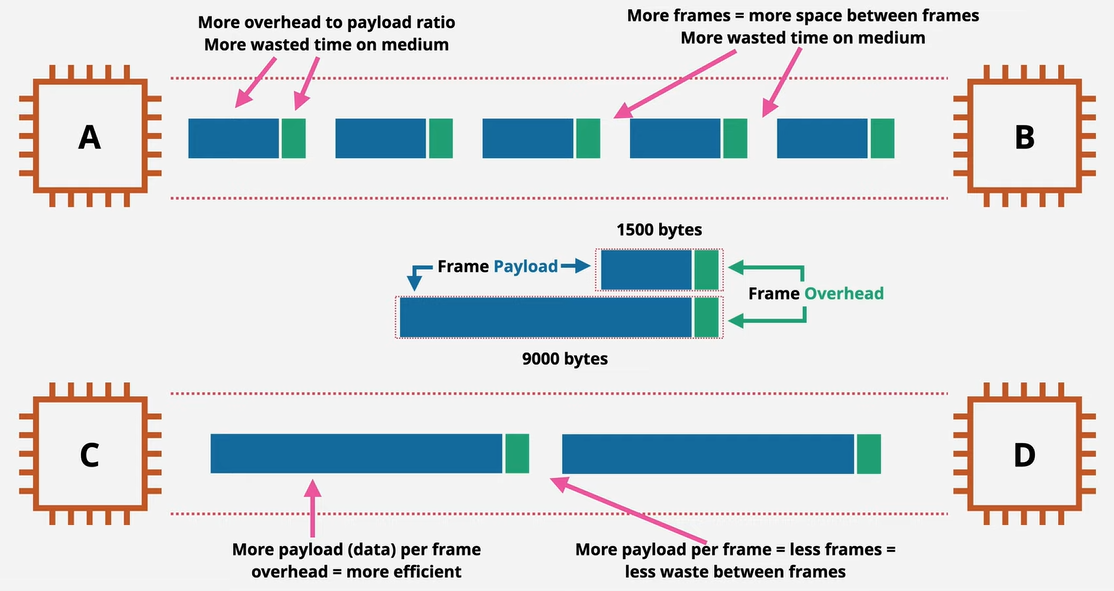
By default, Ethernet frames have a Payload size of 1500 bytes
The max size of the payload is called MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit)
If we have to send more than 1500 bytes in a Frame then we need to allow Jumbo Frames (Frames that are more than 1500 bytes in size)