Part of IEEE 802.1d standard
It was created to prevent loops in the network
In the above network configuration if STP is not used then the switches will end up retransmitting ARP packets to each other resulting in a broadcast storm
TTL is a Layer 3 header property so it can only be decremented by router so the ARP broadcasted packets are never dropped
At switches try to find the best way to reach the root node all other redundant links are blocked
BPDU (Bridge Packet Data Unit)
Switches uses probe signals called BPDU to discover loops (The switch will get its packet back if there was a loop)
It is also used to detect the root bridge on the network
BPDUs are sent out every 2 seconds out every port
BPDUs have two main fields: Priority and MAC Address (aka Bridge ID)
Value of priority is between 0 and 61440 (Default: 32768)
It can only be changed in increments of 4096
Root and Non-root Bridge
STP works be electing a Root and Non-root Bridge
The root bridge acts as the reference point for the entire spanning tree
Bridge ID is used to select the root bridge for the network
Bridge ID is made up of a priority value and a MAC Address
First the priority is checked if it is same for bridges then the MAC Address is checked
The bridge that has the lowest bridge ID becomes the root bridge
There can only be one root bridge all other bridges become non-root bridges
All ports on the root bridge will be forwarding packets (No blocked ports)
Port Types
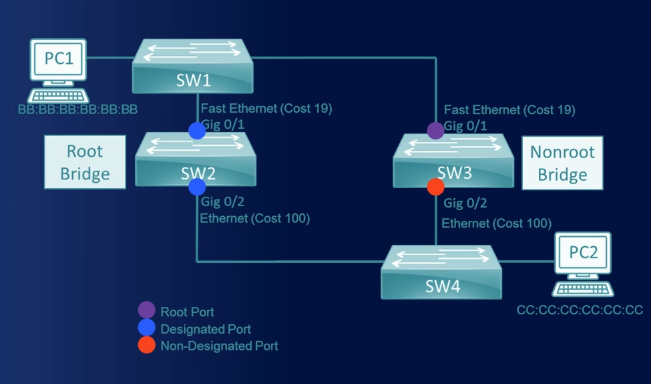
Root Port
Root port is configured on all non-root bridges. Root port carries traffic towards the root bridge
It is the port that connects to the root bridge or if there are multiple paths to the root bridge the path with the lowest cost
If the cost to the root bridge from multiple paths is the same for a switch then the switch with lower bridge ID is selected as the preferred link
If the cost tie still cannot be broken then the lowest port on the switch will be chosen as the root port
Cost is based on the category of the cabling used (High bandwidth cables have low cost)
If there are switches on the path to the root bridge then the switches use BPDU packets to communicate with each other there path cost
For determining the root port the total path cost will be considered
Designated Port
Every network link has to have at least one designated port
All the ports on the root bridge are considered as designated ports
These ports are used for forwarding packets
Designated Port always appear on the link with the blocked port
On a link the switch that has the highest MAC Address will have its port blocked
Non-designated Port
Ports that are going to block the traffic
The Non-designated Port still receive BPDU packets but they are not processed
When a link in the network goes down the Non-designated port can detect this and decides if it needs to transition to a forwarding port
A blocked port transitions between four state when it goes from blocking to forwarding:
Blocking: Receives BPDUs but are not forwarded
Listening: Populates its MAC Address table but does not forward any packet
Learning: Processes BPDUs to determine its role in the Spanning Tree
Forwarding: Forwards frames for operation